Search Provider & Product Reviews
March 9, 2011 Aerocom
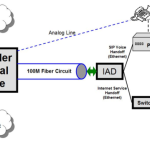
- Definition: Internet access that is brought into a building using fiber optic cables and handed off to the end-user via an Ethernet cable. The minimum speed available is typically 10M and is usually sold in 10M increments, with virtually no limit to the amount of Internet speed a business can purchase.
- Best Fit: A business that has fiber available in their building and needs 10M+, high quality Internet speed and is anticipating needing more than 10M in the near future or at different times of the year.
- Benefits:
- Inexpensive Router. Extremely high bandwidth yet handed off via Ethernet as opposed to needing to purchase an expensive router with single or dual DS3 Interface cards.
- Bandwidth on demand. Depending on the port size purchased, a company can burst their Internet speed above the purchased amount, when needed.
- Fast Scalability. If the capacity is available, increasing the speed of your Ethernet over Fiber Internet connection is much faster than other Internet connectivity products.
- Less Downtime. Fiber optic cables are less prone to service outages than copper cables (i.e. T1 lines).
- Fast Speed. 10M+ Synchronous Download and Upload bandwidth.
- Same speed, all the time. Dedicated bandwidth, not shared with other neighboring customers of that service provider.
- Faster overall performance and less downtime. Ethernet over Fiber Internet connections come with a Service Level Agreement (SLA), that guarantees Network Availability, Packet Loss, Latency and sometimes Jitter.
- Available Features with Select Providers
- Burstable Bandwidth
- Managed Router
- Online bandwidth utilization reporting.
- Automatic Failover to DSL, 4G, etc.
- BGP Routing
[php snippet=7]